From Salon.com
Today, those learning in the one-page-of-talmud-a-day daf yomi cycle begin a new tractate, called Gittin. As its title suggests, it is focussed on the laws of divorce. So let's look at divorce in the western world.
Divorce in the Western WOrld
As you can see in the chart below, the current average rate of divorce in the countries that make up the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is about two per thousand people; in the US the figure is almost three per thousand, while in Israel the figure is just below the OECD average. In many countries the rate is lower than it was in 1995, but in nearly all it is much higher than it was way back in 1970.
Crude divorce rate, 1970, 1995 and 2012. From OECD Family Database.
THE CHANGING RATES OF DIVORCE IN THE US
In the 1970s there was a surge in the divorce rates in the US (and throughout the industrialized world), and in 1977 the sociologist Amir Etzioni issued a dire prediction. If the rates of divorce continued to rise as they had done over the preceding years, "not one American family" would be left intact by the 1990s. But by 1981 the divorce rates levelled off (and more couples were choosing to live together without getting married). By 1998 the divorce rate was 26% lower than it had been in 1979. (This data is found in Marriage, A History by Stephanie Coontz.)
“No party can oblige continuance in contradiction to its end and design.”
In the US, statistics on rates of marriage and divorce are published by the National Center for Health Statistics, which is a branch of the Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. The latest data for the US were published in 2021. It shows that the probability of divorce depends on the length of the marriage. Sadly the probability of divorce increases as the duration of the marriage increases. The probability of a marriage of five years or less ending in divorce is about 20%; the probability of a marriage of twenty years ending in divorce is a massive 48%. And second marriages fare a little worse: by ten years of marriage 32% of those married for the first time will have divorced in the US, compared to 46% of those in their second marriage.
There is some good news. The US divorce has been falling fast in recent years, and it hit a record low in 2019. For every 1,000 marriages in the last year, only 14.9 ended in divorce. This is the lowest rate we have seen in 50 years. It is even slightly lower than 1970, when 15 marriages ended in divorce per 1,000 marriages.
However, the rate of marriage in the US also reached an all-time low in 2019. For every 1,000 unmarried adults in 2019, only 33 got married. This number was 35 a decade ago in 2010 and 86 in 1970. So on balance, maybe things are basically the same.
Divorce rates in the US. Source: The New York Times.
Divorce in Christianity, The UK and the Colonial US
The Church essentially forbade divorce for most of its history, basing itself mostly on Mark 10:9: "what therefore God has joined, let no man put asunder." This left its mark on attitudes towards divorce. (We came across one example of the difficulty in obtaining a divorce when we examined King Henry VIII and his plight to get one of his marriages annulled.) In the United Kingdom of 400 years ago, a divorce required a special Act of its Parliament; this, and its cost made it available only to those with money and privilege. It was only in 1857 that a new law was passed that removed divorce from the control of the Church and made it a civil affair. But husbands and wives were treated very differently by this new law. A husband could obtain a divorce on the grounds of his wife's adultery. But for a wife to obtain a divorce, she had to prove both adultery and an additional "matrimonial offense". The early colonists in the US had similar laws; divorce was allowed only in cases of adultery, habitual drunkenness, desertion, cruelty, or impotence. What we call today "no-fault" divorces have only been around since the 1970s.
JEWISH DIVORCE, THEN AND NOW
It is challenging to get a good count of the rates of divorce in the Jewish communities around the world. One of the rare examples of such data can be found in Jeremy Pfeffer's book From One End of the Earth to the Other, which examines the London Bet Din in the first half of the nineteenth century, and its relationship to the Jewish convicts deported to Australia. (We will return to this fascinating book in our next post.) Pfeffer examined in great detail the marriage and divorce records of the London Bet Din, and discovered that between 1805 and 1855 there were 347 divorces. This turns out to be about one divorce per thousand married Jews, and he notes that the current rate of divorce is "an order of magnitude greater." In fact the current divorce rates in England and Wales are about twelve per thousand married persons, "and there is no reason to suppose that it is significantly lower amongst present day English Jews."
“The indissolubility of marriage is a main principle of English law, asserted without any exception or reserve in the formularies of the Church, in which the parties pledge themselves, either to other, that they will live together so long as they both shall live, and until death shall part them.”
Divorce Rates and Religious Committment
Another study published over 30 years ago reviewed the relationship between rates of divorce and levels of religious commitment. It was based on the 1981 Greater New York Population study which sampled over 4,000 Jewish households, and it made the following observation:
As one might expect, we see the lowest rate of divorce among the Orthodox. In comparison, we see a slight rise among the Conservative, a doubling among the Reform, and a quadrupling for those who do not identify themselves as members of the major denominations. It is the Orthodox community that is most frequently held up as the most effective transmitter of traditional Jewish family values, and these results are consistent with our thesis of a relationship between Jewish commitment and divorce.
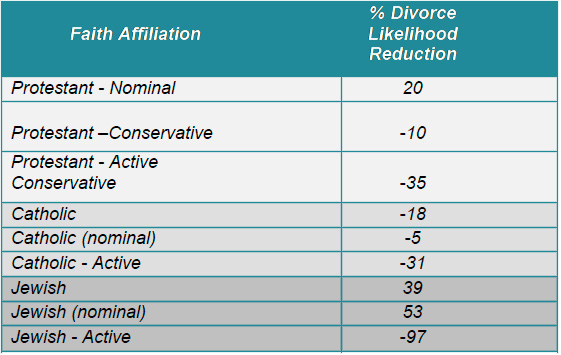
Further support for these findings can be found in more recent work from Focus on the Family ("a global Christian ministry dedicated to helping families thrive"). They report the following relationships between faith affiliation and divorce rates:
From Focus on the Family
Of course we have no idea about whether the lower rate of divorce among active Protestants, Catholics and Jews is because religious practice increases marital harmony or, as a cynic might claim, peer pressure makes those who are more actively religious are reluctant to divorce. Still, a 97% reduction in the divorce rate in those who are "actively Jewish" is pretty impressive.
As we have noted, it took many centuries for secular societies (even in countries that are deeply Catholic) and the church to allow for more equitable divorce laws. For most of that time, Jewish divorce law was in some aspects the most enlightened of any society. It allowed for divorce on the grounds of incompatibility, but at the same time allowed only the husband to control the process. If he did not wish to divorce, no divorce could take place. But the last great change to Jewish divorce law was over 900 years ago, when Rabbenu Gershom forbade a man from divorcing his wife against her will. It is probably time for orthodox Judaism to take another look at the issue.